I have been informed that on March 7th from 6:00am to 6:00pm Central Time Lamar University will be doing some maintenance to replace a faulty UPS component and to do this they will be completely powering down their data center.
Unfortunately, this means that the site will be down during this time. I apologize for any inconvenience this might cause.
Paul
February 18, 2026
Section 3.5 : Derivatives of Trig Functions
13. Where in the range \(\left[ { - 2,7} \right]\) is the function \(f\left( x \right) = 4\cos \left( x \right) - x\) is increasing and decreasing.
Show All Steps Hide All Steps
Start SolutionWe’ll first need the derivative because we know that the derivative will give us the rate of change of the function. Here is the derivative.
\[\require{bbox} \bbox[2pt,border:1px solid black]{{f'\left( x \right) = - 4\sin \left( x \right) - 1}}\] Show Step 2Next, we need to know where the function is not changing and so all we need to do is set the derivative equal to zero and solve.
\[ - 4\sin \left( x \right) - 1 = 0\hspace{0.5in} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.5in}\sin \left( x \right) = - \frac{1}{4}\]A quick calculator computation tells us that,
\[x = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( { - \frac{1}{4}} \right) = - 0.2527\]Recalling our work in the Review chapter on solving trig equations we know that a positive angle corresponding to this solution is : \(x = 2\pi - 0.2527 = 6.0305\). Either can be used, but we will use the positive angle.
Also, from a quick check on a unit circle we can see that \(x = \pi + 0.2527 = 3.3943\) will be a second solution.
Putting all of this together and we can see that the derivative will be zero at,
\[x = 6.0305 + 2\pi n\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{\mbox{and}}\hspace{0.25in}x = 3.3943 + 2\pi n\hspace{0.25in}\,n = 0, \pm 1, \pm 2, \pm 3, \ldots \]Finally, all we need to so is plug in some \(n\)’s to determine which solutions fall in the interval we are working on, \(\left[ { - 2,7} \right]\).
So, in the interval \(\left[ { - 2,7} \right]\) the function will stop changing at the following three points.
\[x = - 0.2527,\,\,\,\,\,3.3943,\,\,\,\,6.0305\] Show Step 3To get the answer to this problem all we need to know is where the derivative is positive (and hence the function is increasing) or negative (and hence the function is decreasing). Because the derivative is continuous we know that the only place it can change sign is where the derivative is zero. So, as we did in this section a quick number line will give us the sign of the derivative for the various intervals.
Here is the number line for this problem.
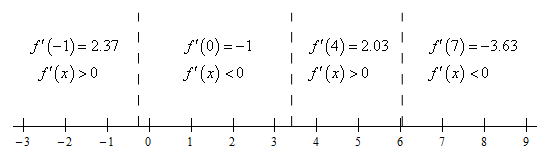
From this we get the following increasing/decreasing information.
\[\require{bbox} \bbox[2pt,border:1px solid black]{\begin{align*}{\mbox{Increasing :}}&\,\, - 2 \le x < - 0.2527,\,\,\,\,3.3943 < x < 6.0305\\ {\mbox{Decreasing :}}&\,\, - 0.2527 < x < 3.3943,\,\,\,\,6.0305 < x \le 7\end{align*}}\]Note that because we’ve only looked at what is happening in the interval \(\left[ { - 2,7} \right]\) we can’t say anything about the increasing/decreasing nature of the function outside of this interval.