I have been informed that on March 7th from 6:00am to 6:00pm Central Time Lamar University will be doing some maintenance to replace a faulty UPS component and to do this they will be completely powering down their data center.
Unfortunately, this means that the site will be down during this time. I apologize for any inconvenience this might cause.
Paul
February 18, 2026
Section 1.3 : Trig Functions
11. Determine the exact value of \(\displaystyle \sec \left( {\frac{{29\pi }}{4}} \right)\) without using a calculator.
Show All Steps Hide All Steps
First we can notice that \(\frac{{5\pi }}{4} + 6\pi = \frac{{29\pi }}{4}\) and recalling that \(6\pi \) is three complete revolutions we can see that \(\frac{{29\pi }}{4}\) and \(\frac{{5\pi }}{4}\) represent the same angle. Next, note that \(\pi + \frac{\pi }{4} = \frac{{5\pi }}{4}\) and so the line representing \(\frac{{5\pi }}{4}\) will form an angle of \(\frac{\pi }{4}\) with the negative \(x\)-axis in the third quadrant and we’ll have the following unit circle for this problem.
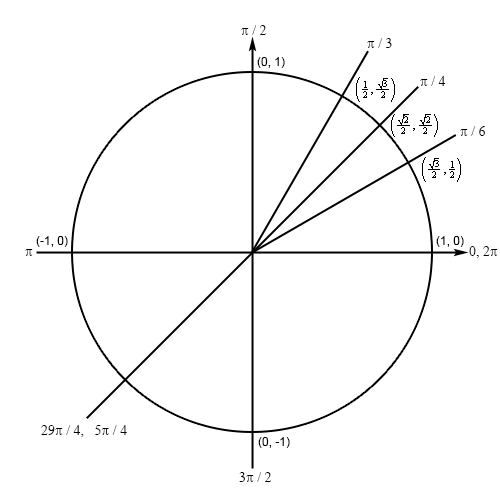
The line representing \(\frac{{95\pi }}{4}\) is a mirror image of the line representing \(\frac{\pi }{4}\) and so the coordinates for \(\frac{{29\pi }}{4}\) will be the same as the coordinates for \(\frac{\pi }{4}\) except that both coordinates will now be negative. So, our new coordinates will then be \(\left( { - \frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}, - \frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}} \right)\) and so the answer is,
\[\sec \left( \frac{29\pi }{4} \right)=\frac{1}{\cos \left( \frac{29\pi }{4} \right)}=\frac{1}{-{}^{\sqrt{2}}/{}_{2}}=-\frac{2}{\sqrt{2}}=-\sqrt{2}\]